Εμπεδοκλής έγραψε: ↑10 Ιαν 2022, 17:59
Wikipedia, η χαρά του αμόρφωτου ή ημιμαθούς.
Πάμε τώρα σε κάτι πιο επιστημονικό.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25289716/The objective of this study was to describe the characteristics of mortalities from 2007 to 2013 in active (during career) and recently retired (post career) professional footballers. An observational prospective study was conducted. From 2007, the World Footballers' Union (FIFPro) and its related national footballers' unions (more than 70 countries distributed across all continents) collected descriptive data (football-related, cause, etc.) on mortality of active (during career) and recently retired (postcareer before reaching 45 years of age) professional footballers by means of several official sources. A total of 214 deaths were recorded among active and recently retired professional footballers, leading to an overall mortality rate of 0.47 per 1000 footballers per year. Of the 214 deaths, 183 were recorded among active players and 31 among recently retired players. Among the active players, 17% of the fatalities were related to football participation. Disease was the leading cause of death among professional footballers (55%), of which up to 33% accounted for suspected cardiac pathology. Accidents accounted for 25% of the overall deaths, and suicide for 11%. From 2007 to 2013, 214 deaths were recorded among active (during career) and recently retired (post career) professional footballers. Leading cause of death was disease (55%), one third of which were accounted for by suspected cardiac pathology, while accidents accounted for 25% of all deaths, and suicide for 11%. Attention to the predictive validity and application of heart-related precompetition medical assessment should be given, and mental health support should be developed and implemented both during and after a professional football career to prevent potential suicidal behaviors.
https://nccsir.unc.edu/wp-content/uploa ... -FINAL.pdf
Και μετά την επιστημονική απάντηση, ας γυρίσουμε και πάλι στο επίπεδο του phorum.

επίσης
https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMra022783
βάζω μια περίληψη γιατί θέλει (free) account:
Sudden Death in Young AthletesCardiovascular Causes of Sudden Death
Although the overall population of athletes is at generally low risk for sudden death,5,16 a number of largely congenital but clinically unsuspected cardiovascular diseases have been causally linked to sudden death in young trained athletes, usually in association with physical exertion. In large autopsy-based surveys of populations of athletes in the United States, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy has consistently been the single most common cardiovascular cause of sudden death (Table 1), accounting for about one third of these events in prior reports.
Athletic-Field Risks Unrelated to Cardiovascular Disease
COMMOTIO CORDIS
Most notable examples of sudden death in athletes without antecedent heart disease occur as a result of blunt, nonpenetrating, and innocent-appearing blows to the chest that produce ventricular fibrillation unassociated with structural injury to the ribs, sternum, or heart.
The precordial blows that trigger commotio cordis are often not perceived as unusual for the sporting event involved or of sufficient magnitude to cause death.
OTHER RISKS
A small number of sudden deaths are reported each year among athletes that are due not to cardiac causes but to factors such as extreme heat, leading to hyperthermia and central nervous system dysfunction (heat stroke); head and spine trauma (usually among football players and pole vaulters); uncontrolled bronchial asthma; ruptured cerebral-artery aneurysm; sickle cell trait; and nonpenetrating blows to the neck by hockey pucks, which trigger rupture of the vertebral artery and subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Sudden unexpected death, nonfatal stroke, and acute myocardial infarction in trained athletes have been attributed to the abuse of cocaine, anabolic steroids, and dietary and nutritional supplements. Dietary supplements such as ma huang, an herbal source of ephedrine (i.e., elemental ephedra), which is a potentially arrhythmogenic cardiac stimulant, are often taken to enhance athletic performance or to mask the presence of other drugs during testing. Causal linkage between the use of dietary supplements and cardiovascular events is largely inferential, based on a close temporal relation between the ingestion of the compound and adverse events in otherwise healthy people.

το'χει και στην wiki για τον Kauldron:
Sudden cardiac death of athletesHowever, a population as large as the United States will experience the sudden cardiac death of a competitive athlete at the average rate of one every three days, often with significant local media coverage heightening public attention.[17]
κατά τ'άλλα από την μελέτη τού Εμπέδοκλα για ποδοσφαιριστές βγαίνει ετήσιο ρίσκο για θάνατο παίζοντας μπάλα πρπ 80/εκ.
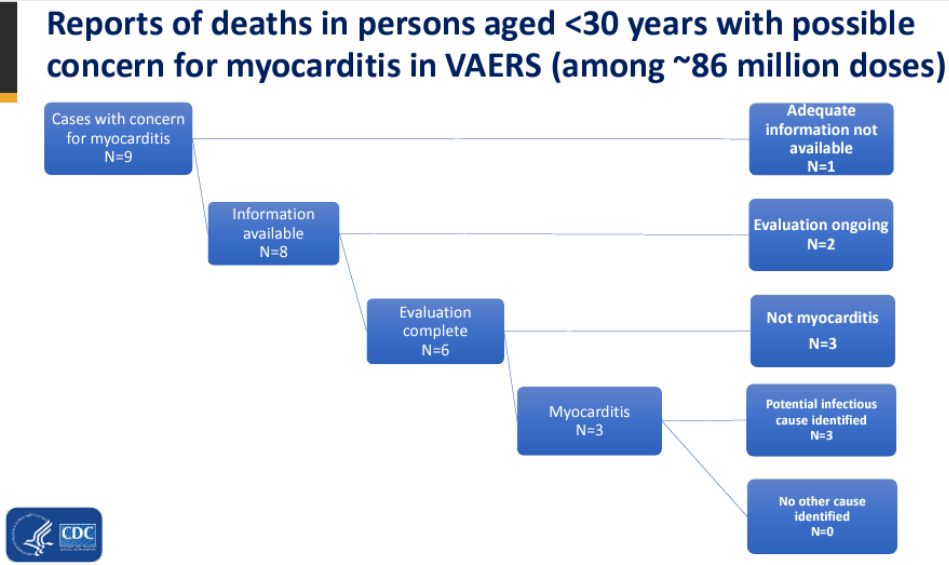
στο VAERS ως τον Νοέμβριο είχαν καταγραφεί 9 περιπτώσεις θανάτων με υποψία μυοκαρδίτιδας σε 86εκ δόσεις. αν υποθέσουμε ότι ισχύουν όλες αλά ψεκ (δεν είχε επιβεβαιωθεί καμμία) το ρίσκο είναι 0.1/εκ. λογικά οι αθλητές έχουν αυξημένο ρίσκο, έστω 10Χ = 1/εκ.
συμπέρασμα: πιθανόν να αυξήθηκαν κατά 1% οι ξαφνικοί θάνατοι ποδοσφαιριστών το '21 λόγω εμβολιασμού, αν εμβολιάστηκαν σχεδόν όλοι. αλλά όσο και να αυξήθηκαν το μόνο σίγουρο είναι ότι αυτό δεν μπορεί να διαπιστωθεί από την.. λίστα τής wiki.

έλεος με την ψέκα, έχει πέσει και η υποστάθμη με τον Χελώνο στο πόδι τού Αρίστου.